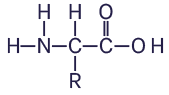PKU is a genetic condition. In individuals with PKU, an amino acid; phenylalanine (phe), can’t be broken down in the body so it builds up to high levels in the blood. These high levels are toxic to the brain.
The foods we eat contain different types of nutrients including, carbohydrate, fat, and protein.
For individuals with PKU, protein is the crucial nutrient as this contains amino acids, one of which is phe. Therefore for people with PKU the protein intake needs to be counted in measured portions and intake needs to be monitored closely.
Maintaining phe levels within the normal range will be achieved by following a low protein diet. The person with PKU will also require a protein substitute and a small amount of natural protein.
The 4 main components of the low protein diet for PKU, are outlined below.
Those with PKU need a small amount of natural protein to provide the right amount of phe which will help support their normal growth and development.
Protein intake is extremely restricted in the diet for PKU, and so to meet daily protein requirements a protein substitute is essential.
Certain foods contain little or no phe. These can be eaten "freely" and do not need to be protein counted. Speak to your dietitian about which foods these are.
There are specially made foods that are low in protein (and therefore low in phe), these include: